Describe the Cohesion-tension Theory of Water Transport in the Xylem
Water from the soil reaches the plants xylem of roots against. The cohesion of water One way to visualize the importance of cohesion and adhesion in water movement through xylem is to look at how water moves through narrow tubes called capillary.
Cohesion Tension Theory Study Solutions
The water column cannot be broken or pulled away.

. At night when stomata shut and transpiration stops the water is held in the stem and leaf by the adhesion of water to the cell walls of the. Xylem vessels become narrower. The cohesion-tension theory describes how water moves from the roots to the leaf.
Water from the roots is pulled up by this tension. Plants transpire by the Cohesion Tension theory. Water molecules stick together via hydrogen bonds in a process known as COHESION.
The cohesion-tension theory suggests that water is obtained in plants from soil due to the fact that water is cohesive and so is able to be drawn up from soil particles into the root hairs via. A student used a potometer to. Water is consequently pulled upwards as it.
5 Total 10 marks Q2. As the name suggests the cohesion theory is based on the. Transpiration is ultimately the main driver of water movement in xylem.
This theory was given by Henry Dixon in 1914. It is believed that this process results in the. Osmosis causes water to enter the xylem of roots from the soil.
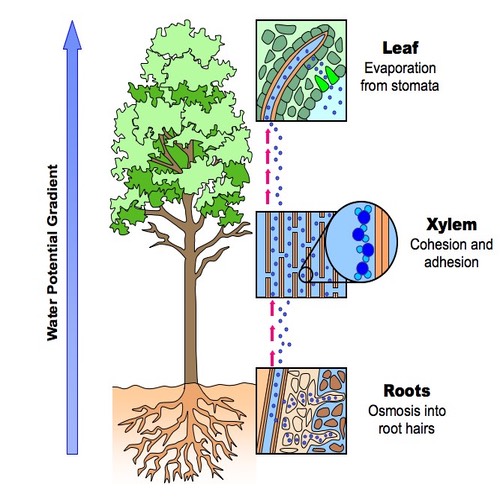
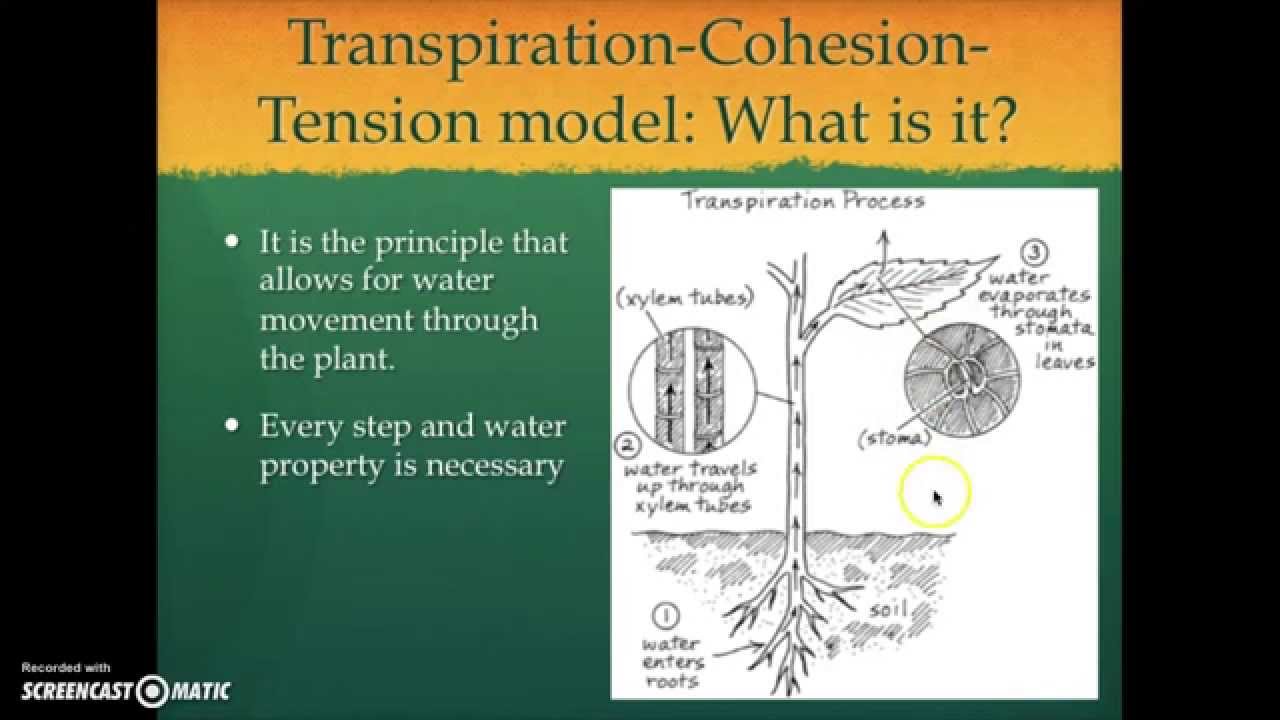
The cohesion-tension model works like this. A Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem. Transpiration of water through stomata creates low potential at the top of the xylem.
Evaporation exerts force causing tension in water columns Cohesion holds water column together Adhesion between walls of the xylem and the water molecules results in a pulling. According to the widely accepted Cohesion Theory water is pulled by transpiration from the roots through the xylem to the leaves. Tension negative pressure on water in xylem creates inward pull on walls of xylem vessel.
Water lost from leaf because of transpiration evaporation of water molecules diffusion from mesophyll leaf. 2 The entire column of water in the xylem is stretched. The widely supported cohesiontension theory of water transport explains the importance of a continuous water column and the mechanism of long-distance ascent of sap.
Outline the role of the xylem in the movement of water through a plant describe theories for the ascent of water including root pressure capillary action and imbibition explain how the. Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem. Transpiration evaporation occurs because stomata are open to allow.
This is often referred to as the cohesionadhesion or cohesiontension theory of water transport. 5 b Describe how mRNA is produced in a plant cell. Up to 24 cash back The Cohesion-Tension Theory The major mechanism for long-distance water transport is described by the cohesion-tension theory whereby the driving force of.
CohesionAdhesion or CohesionTension Theory of Water Movement. The attraction of water to other water molecules or cohesion allows water to pull other water molecules up through the xylem. A theory that describes the water movement from the roots of the plants to its leaves is the cohesion tension mechanism.
Due to adhesion of water molecules to walls of xylem. Water diffuse out of the stomata this creates tension in the xylem. Due to the hydrogen.
Cohesion tension theory of water transport in the xylem of plants. Cohesion- Is the sticking of similar molecules to each other. The water in the xylem is said to be under tension.
This theory is quite convincing and has been widely accepted. The water is filled inside the xylem capillaries and due to cohesion and adhesion properties of water it forms a continuous water column.

17 1 3 Cohesion Tension Theory Biology Libretexts

17 1 3 Cohesion Tension Theory Biology Libretexts

Comments
Post a Comment